Introduction
In this article I am attempting to illustrate how to use Microsoft Enterprise Library data using the MVC 2 pattern.
Model, Views Controller (MVC) separates the modelling of the domain, the presentation and the actions based on user input into three classes.
In this article I am attempting to illustrate how to use Microsoft Enterprise Library data using the MVC 2 pattern.
Model, Views Controller (MVC) separates the modelling of the domain, the presentation and the actions based on user input into three classes.
- Model: The model manages the behaviour and data of the application domain, responds to requests for information about its state (usually from the view), and responds to instructions to change state (usually from the controller).
- Controller: The controller interprets the mouse and keyboard inputs from the user, informing the model and/or the view to change as appropriate.
- View: The view manages the display of information.
DAAB: The Data Access Application Block encapsulates the performance and resource management best practices for accessing Microsoft SQL Server databases. It can easily be used as a building block in your own .NET-based application. If you use it then you will reduce the amount of custom code you need to create, test, and maintain.
You can download DAAB from here: http://www.microsoft.com/downloads/details.aspx?familyid=f63d1f0a-9877-4a7b-88ec-0426b48df275&displaylang=en
Getting Started
Make a new project using Visual Studio 2010 and select "ASP.NET MVC 2 Web Application".
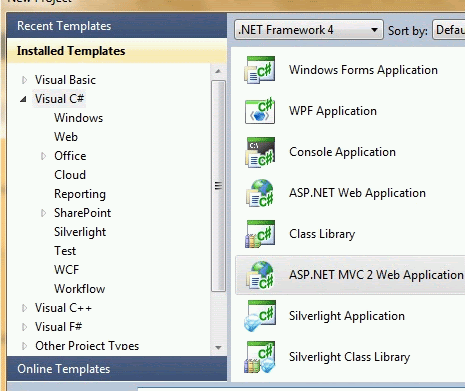
Image 1.
You can create a unit test project if you want to.
Note: If you are using the Standard or Express editions of Visual Studio then the Create Unit Test Project dialog box is not displayed. Instead, the new MVC application project is generated without a test project.
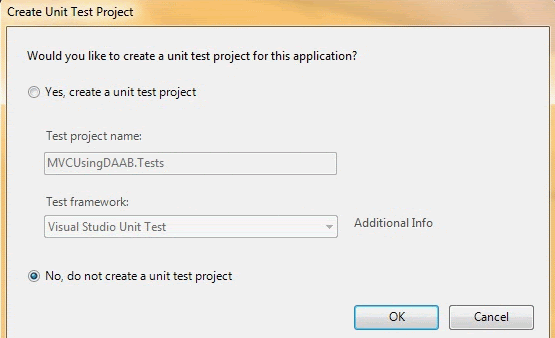
Image 2.
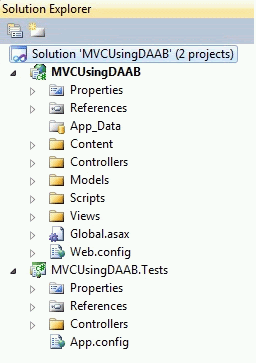
Image 3.
The Unit test project has already added the reference of the web project.
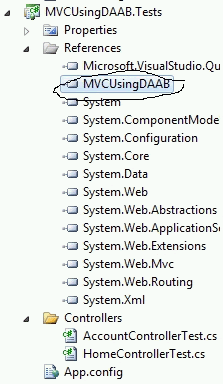
Image 4.
The folder structure of an MVC project differs from that of an ASP.NET Web site project. The MVC project contains the following folders: First of all you need to add a reference for "Microsoft.Practices.EnterpriseLibrary.Data.dll".
Then add a config section in the configuration file.
<configSections>
<sectionname="dataConfiguration"
type="Microsoft.Practices.EnterpriseLibrary.Data.Configuration.DatabaseSettings, Microsoft.Practices.EnterpriseLibrary.Data" />
</configSections>
Here is the connection string:
<connectionStrings>
<addname="NorthWNDConnectionString" connectionString="data source=.\SQLEXPRESS;Integrated Security=SSPI;AttachDBFilename=|DataDirectory|NORTHWND.MDF;User Instance=true"
providerName="System.Data.SqlClient" />
<addname="ApplicationServices"
connectionString="data source=.\SQLEXPRESS;Integrated Security=SSPI;AttachDBFilename=|DataDirectory|aspnetdb.mdf;User Instance=true"
providerName="System.Data.SqlClient" />
</connectionStrings>
Now add a controller class to the Controller folder, as in the following:
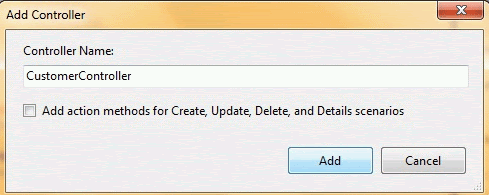
Image 5.
CustomerController.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Web;
using System.Web.Mvc;
You can download DAAB from here: http://www.microsoft.com/downloads/details.aspx?familyid=f63d1f0a-9877-4a7b-88ec-0426b48df275&displaylang=en
Getting Started
Make a new project using Visual Studio 2010 and select "ASP.NET MVC 2 Web Application".
Image 1.
You can create a unit test project if you want to.
Note: If you are using the Standard or Express editions of Visual Studio then the Create Unit Test Project dialog box is not displayed. Instead, the new MVC application project is generated without a test project.
Image 2.
Image 3.
The Unit test project has already added the reference of the web project.
Image 4.
The folder structure of an MVC project differs from that of an ASP.NET Web site project. The MVC project contains the following folders: First of all you need to add a reference for "Microsoft.Practices.EnterpriseLibrary.Data.dll".
Then add a config section in the configuration file.
<configSections>
<sectionname="dataConfiguration"
type="Microsoft.Practices.EnterpriseLibrary.Data.Configuration.DatabaseSettings, Microsoft.Practices.EnterpriseLibrary.Data" />
</configSections>
Here is the connection string:
<connectionStrings>
<addname="NorthWNDConnectionString" connectionString="data source=.\SQLEXPRESS;Integrated Security=SSPI;AttachDBFilename=|DataDirectory|NORTHWND.MDF;User Instance=true"
providerName="System.Data.SqlClient" />
<addname="ApplicationServices"
connectionString="data source=.\SQLEXPRESS;Integrated Security=SSPI;AttachDBFilename=|DataDirectory|aspnetdb.mdf;User Instance=true"
providerName="System.Data.SqlClient" />
</connectionStrings>
Now add a controller class to the Controller folder, as in the following:
Image 5.
CustomerController.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Web;
using System.Web.Mvc;
- Content for content support files. This folder contains the Cascading Style Sheet (.css file) for the application.
- Controllers for the controller files. This folder contains the application's sample controllers, which are named AccountController and HomeController. The AccountController class contains login logic for the application. The HomeController class contains logic that is called by default when the application starts.
- Models for the data-model files such as LINQ-to-SQL .dbml files or data-entity files.
- Scripts for the script files, such as those that support ASP.NET AJAX and jQuery.
- Views for the view page files. This folder contains three subfolders: Account, Home, and Shared. The Account folder contains views that are used as the UI for logging in and changing passwords. The Home folder contains an Index view (the default starting page for the application) and an about page view. The Shared folder contains the master-page view for the application.
namespace MVCUsingDAAB.Controllers
{
public class Default1Controller : Controller {
//
// GET: /Default1/
{
public class Default1Controller : Controller {
//
// GET: /Default1/
public ActionResult Index()
{
return View();
}
}
}
Add a Tab to the master page menu:
<li><%:Html.ActionLink("Customers", "Index", "Customer")%></li>

Image 6.
Let me copy my models classes code first:
Models/Customer.cs
using System;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Web;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
{
return View();
}
}
}
Add a Tab to the master page menu:
<li><%:Html.ActionLink("Customers", "Index", "Customer")%></li>
Image 6.
Let me copy my models classes code first:
Models/Customer.cs
using System;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Web;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
namespace MVCUsingDAAB.Models
{
{
public class Customers {
///<summary>
/// Gets the CustomerID.///</summary>public string CustomerID { get; set; }
///<summary>
/// Gets the CompanyName.///</summary>public string CompanyName { get; set; }
///<summary>
/// Gets the ContactName.///</summary>public string ContactName { get; set; }
///<summary>
/// Gets the Address.///</summary>public string Address { get; set; }
///<summary>
/// Gets the City.///</summary>public string City { get; set; }
///<summary>
/// Gets the CustomerID.///</summary>public string CustomerID { get; set; }
///<summary>
/// Gets the CompanyName.///</summary>public string CompanyName { get; set; }
///<summary>
/// Gets the ContactName.///</summary>public string ContactName { get; set; }
///<summary>
/// Gets the Address.///</summary>public string Address { get; set; }
///<summary>
/// Gets the City.///</summary>public string City { get; set; }
public Customers(string id, stringcompanyname, stringcontactname, string address, string city)
{
CustomerID = id;
CompanyName = companyname;
ContactName = contactname;
Address = address;
City = city;
}
public Customers()
{
}
}
}
Models/CustomerModel.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
{
CustomerID = id;
CompanyName = companyname;
ContactName = contactname;
Address = address;
City = city;
}
public Customers()
{
}
}
}
Models/CustomerModel.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace MVCUsingDAAB.Models
{
interface ICustomerModel {
List<Customers>GetCustomers();
}
}
{
interface ICustomerModel {
List<Customers>GetCustomers();
}
}
Models/CustomerListContainerViewModel.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Web;
using System.Web.Mvc;
using MvcContrib.Pagination;
using MvcContrib.UI.Grid;
using System.Data;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Web;
using System.Web.Mvc;
using MvcContrib.Pagination;
using MvcContrib.UI.Grid;
using System.Data;
namespace MVCUsingDAAB.Models
{
public class CustomerListContainerViewModel {
public IPagination<Customers>CustomerPagedList { get; set; }
}
}
Models/ICustomerModel.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
{
public class CustomerListContainerViewModel {
public IPagination<Customers>CustomerPagedList { get; set; }
}
}
Models/ICustomerModel.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace MVCUsingDAAB.Models
{
interface ICustomerModel {
List<Customers>GetCustomers();
}
}
{
interface ICustomerModel {
List<Customers>GetCustomers();
}
}
Models/CustomerListContainerViewModel.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
usingSystem.Text;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
usingSystem.Text;
namespace MVCUsingDAAB.Models
{
interface ICustomerModel {
List<Customers>GetCustomers();
}
}
Controller/CustomerController.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Web;
using System.Web.Mvc;
using Microsoft.Practices.EnterpriseLibrary.Data;
using System.Configuration;
using System.Data;
using System.Data.Common;
using MVCUsingDAAB.Models;
using MvcContrib.Pagination;
{
interface ICustomerModel {
List<Customers>GetCustomers();
}
}
Controller/CustomerController.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Web;
using System.Web.Mvc;
using Microsoft.Practices.EnterpriseLibrary.Data;
using System.Configuration;
using System.Data;
using System.Data.Common;
using MVCUsingDAAB.Models;
using MvcContrib.Pagination;
namespace MVCUsingDAAB.Controllers
{
public class CustomerController : Controller {
//
// GET: /Customer/ICustomerModel customerRepository;
public CustomerController()
{
customerRepository = newCustomerModel();
}
public ActionResult Index(int? page)
{
var customerPagedList = customerRepository.GetCustomers().AsPagination(page ?? 1, 10);
var customerListContainer = new CustomerListContainerViewModel {
CustomerPagedList = customerPagedList,
};
return View(customerListContainer);
}
{
public class CustomerController : Controller {
//
// GET: /Customer/ICustomerModel customerRepository;
public CustomerController()
{
customerRepository = newCustomerModel();
}
public ActionResult Index(int? page)
{
var customerPagedList = customerRepository.GetCustomers().AsPagination(page ?? 1, 10);
var customerListContainer = new CustomerListContainerViewModel {
CustomerPagedList = customerPagedList,
};
return View(customerListContainer);
}
}
}
Views/AllCustomers.ascx
<%@ControlLanguage="C#" Inherits="System.Web.Mvc.ViewUserControl<MVCUsingDAAB.Models.CustomerListContainerViewModel>"%>
<%@ImportNamespace="MvcContrib.UI.Grid"%>
<%@ImportNamespace="MVCUsingDAAB.Models"%>
<%@ImportNamespace="MvcContrib.UI.Grid.ActionSyntax"%>
<%=Html.Grid(Model.CustomerPagedList).AutoGenerateColumns()
.Columns(column => {
column.For(a =>Html.ActionLink("Details", "Details", new { id = a.CustomerID })).InsertAt(0).Encode(false);
})
.Attributes(@class =>"table-list")
%>
Views/Shared/Page.ascx
<%@ControlLanguage="C#"Inherits="System.Web.Mvc.ViewUserControl<MvcContrib.Pagination.IPagination>"%>
<%@ImportNamespace="MvcContrib.UI.Pager"%><p/><%=Html.Pager(Model)
.First("First")
.Last("Last")
.Next("Next")
.Previous("Previous") %><p/>
Views/Index.aspx
<%@PageTitle=""Language="C#" MasterPageFile="~/Views/Shared/Site.Master" Inherits="System.Web.Mvc.ViewPage<MVCUsingDAAB.Models.CustomerListContainerViewModel>"%><asp:ContentID="Content1"ContentPlaceHolderID="TitleContent"runat="server"> Index
</asp:Content>
<asp:ContentID="Content2"ContentPlaceHolderID="MainContent"runat="server">
<h2>Customers</h2><%Html.RenderPartial("AllCustomers", Model); %><%Html.RenderPartial("Pager", Model.CustomerPagedList); %></asp:Content>
Now build the project and see the result like this:
}
Views/AllCustomers.ascx
<%@ControlLanguage="C#" Inherits="System.Web.Mvc.ViewUserControl<MVCUsingDAAB.Models.CustomerListContainerViewModel>"%>
<%@ImportNamespace="MvcContrib.UI.Grid"%>
<%@ImportNamespace="MVCUsingDAAB.Models"%>
<%@ImportNamespace="MvcContrib.UI.Grid.ActionSyntax"%>
<%=Html.Grid(Model.CustomerPagedList).AutoGenerateColumns()
.Columns(column => {
column.For(a =>Html.ActionLink("Details", "Details", new { id = a.CustomerID })).InsertAt(0).Encode(false);
})
.Attributes(@class =>"table-list")
%>
Views/Shared/Page.ascx
<%@ControlLanguage="C#"Inherits="System.Web.Mvc.ViewUserControl<MvcContrib.Pagination.IPagination>"%>
<%@ImportNamespace="MvcContrib.UI.Pager"%><p/><%=Html.Pager(Model)
.First("First")
.Last("Last")
.Next("Next")
.Previous("Previous") %><p/>
Views/Index.aspx
<%@PageTitle=""Language="C#" MasterPageFile="~/Views/Shared/Site.Master" Inherits="System.Web.Mvc.ViewPage<MVCUsingDAAB.Models.CustomerListContainerViewModel>"%><asp:ContentID="Content1"ContentPlaceHolderID="TitleContent"runat="server"> Index
</asp:Content>
<asp:ContentID="Content2"ContentPlaceHolderID="MainContent"runat="server">
<h2>Customers</h2><%Html.RenderPartial("AllCustomers", Model); %><%Html.RenderPartial("Pager", Model.CustomerPagedList); %></asp:Content>
Now build the project and see the result like this:
Source collected from CSharpCorner.com
http://www.c-sharpcorner.com/uploadfile/raj1979/data-access-application-block-using-mvc-2-pattern/
No comments:
Post a Comment